

Write blockDim.x output elements to global memory.Read (blockDim.x + 2 * radius) input elements from global memory to shared memory.Data is not visible to threads in other blocks.

Declare using _shared_, allocated per block.By opposition to device memory, referred to as global memory.Within a block, threads share data via shared memory.
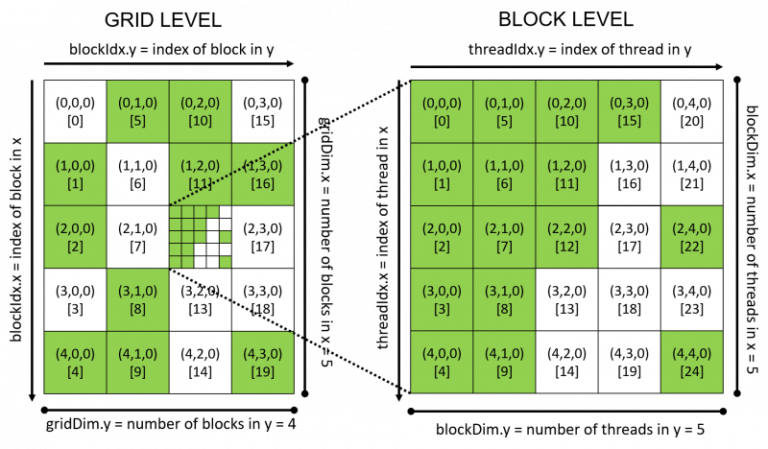
Data is shared between threads in a block.Use _shared_ to declare a variable/array in shared memory Int index = threadIdx.x + blockIdx.x * blockDim.x When we consider a thread block, threadIdx and blockDim standard variables in CUDA can be considered very important. One thread block consists of set of threads.Unlike parallel blocks, threads have mechanisms to efficiently: A block can be split into parallel threads.We will use 'blocks' and 'threads' to implement parallelism. GPU computing is about massive parallelism.The compute capability of a device describes its architecture, e.g. Device The GPU and its memory (device memory).Host The CPU and its memory (host memory).GPU Activity Monitor – NVIDIA Jetson TX Dev Kit :.Avoiding Pitfalls when Using NVIDIA GPUs :.An Easy Introduction to CUDA C and C++ :.Udacity - Intro to Parallel Programming.CUDA Zone – tools, training and webinars :.BOOK : Introduction to Parallel Computing.BOOK : Designing and Building Parallel Programs :.
 cudaMemcpy() vs cudaMemcpyAsync(), cudaDeviceSynchronize(). Manage communication and synchronization. _global_, >, blockIdx, threadIdx, blockDim. When using CUDA, developers program in popular languages such as C, C++, Fortran, Python and MATLAB and express parallelism through extensions in the form of a few basic keywords.ĬUDA accelerates applications across a wide range of domains from image processing, to deep learning, numerical analytics and computational science. In GPU-accelerated applications, the sequential part of the workload runs on the CPU – which is optimized for single-threaded performance – while the compute intensive portion of the application runs on thousands of GPU cores in parallel. With CUDA, developers are able to dramatically speed up computing applications by harnessing the power of GPUs. IntroductionĬUDA® is a parallel computing platform and programming model developed by NVIDIA for general computing on graphical processing units (GPUs). I would be clear where the configuration of the threads has been defined, and the 1D, 2D and 3D access pattern depends on how you are interpreting your data and also how you are accessing them by 1D, 2D and 3D blocks of threads.This repository contains notes and examples to get started Parallel Computing with CUDA. To sumup, it does it matter if you use a dim3 structure. Int y = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y īecause blockIdx.y and threadIdx.y will be zero. So, in both cases: dim3 blockDims(512) and myKernel>(.) you will always have access to threadIdx.y and threadIdx.z.Īs the thread ids start at zero, you can calculate a memory position as a row major order using also the ydimension: int x = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x The same happens for the blocks and the grid. When defining a variable of type dim3, any component left unspecified is initialized to 1. However, the access pattern depends on how you are interpreting your data and also how you are accessing them by 1D, 2D and 3D blocks of threads.ĭim3 is an integer vector type based on uint3 that is used to specify dimensions. The memory is always a 1D continuous space of bytes. The way you arrange the data in memory is independently on how you would configure the threads of your kernel.
cudaMemcpy() vs cudaMemcpyAsync(), cudaDeviceSynchronize(). Manage communication and synchronization. _global_, >, blockIdx, threadIdx, blockDim. When using CUDA, developers program in popular languages such as C, C++, Fortran, Python and MATLAB and express parallelism through extensions in the form of a few basic keywords.ĬUDA accelerates applications across a wide range of domains from image processing, to deep learning, numerical analytics and computational science. In GPU-accelerated applications, the sequential part of the workload runs on the CPU – which is optimized for single-threaded performance – while the compute intensive portion of the application runs on thousands of GPU cores in parallel. With CUDA, developers are able to dramatically speed up computing applications by harnessing the power of GPUs. IntroductionĬUDA® is a parallel computing platform and programming model developed by NVIDIA for general computing on graphical processing units (GPUs). I would be clear where the configuration of the threads has been defined, and the 1D, 2D and 3D access pattern depends on how you are interpreting your data and also how you are accessing them by 1D, 2D and 3D blocks of threads.This repository contains notes and examples to get started Parallel Computing with CUDA. To sumup, it does it matter if you use a dim3 structure. Int y = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y īecause blockIdx.y and threadIdx.y will be zero. So, in both cases: dim3 blockDims(512) and myKernel>(.) you will always have access to threadIdx.y and threadIdx.z.Īs the thread ids start at zero, you can calculate a memory position as a row major order using also the ydimension: int x = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x The same happens for the blocks and the grid. When defining a variable of type dim3, any component left unspecified is initialized to 1. However, the access pattern depends on how you are interpreting your data and also how you are accessing them by 1D, 2D and 3D blocks of threads.ĭim3 is an integer vector type based on uint3 that is used to specify dimensions. The memory is always a 1D continuous space of bytes. The way you arrange the data in memory is independently on how you would configure the threads of your kernel.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
